Regulators did take steps to address the concerns raised by critics, including limiting the number of weed delivery licenses any company can own to two.
The commission also voted to ban third-party marijuana delivery technology platforms — such as Eaze and Lantern, an offshoot of alcohol delivery firm Drizly — from having a “financial interest” in more than one cannabis delivery licensee. The policy is meant to prevent the popular websites from preferentially steering consumers to delivery companies they’re invested in while freezing out independent operators; it could also help assuage brick-and-mortar dispensary owners who feared a large Amazon-like platform would back numerous delivery firms and dominate the market.
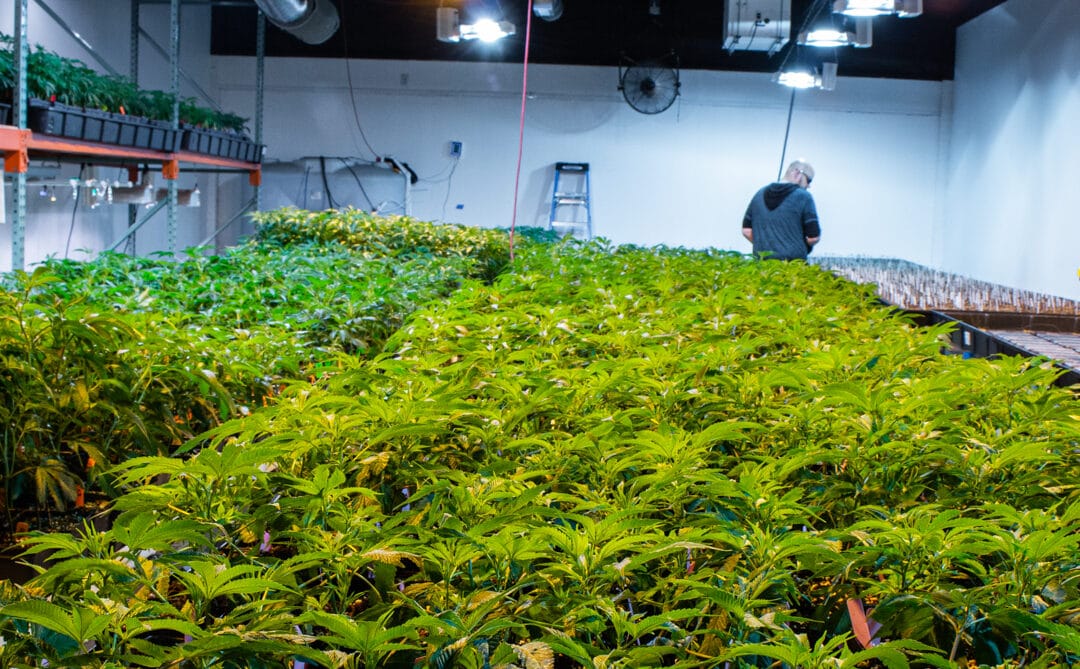
Commissioners further opted to ban what they deemed the “ice cream truck” model, under which weed delivery operators might have prepositioned vans loaded with packaged pot products in strategic locations to fulfill anticipated orders. Instead, every order must originate from the company’s warehouse. And they left in place earlier security restrictions, including a mandate that two workers must ride in every delivery vehicle and a prohibition on delivering recreational marijuana to cities and towns that have banned retail marijuana storefronts. (Medical marijuana deliveries have long been allowed anywhere in the state.)
Commissioner Jen Flanagan, who has long opposed launching delivery operations on public safety and health grounds, made a last-ditch attempt to delay the program’s launch until 2023.
However, her motion failed 3-1, with Hoffman noting that the commission had originally planned to launch deliveries in 2018 before pulling back under pressure from Governor Charlie Baker and others who urged the agency to “crawl before it walks.” Outgoing Commissioner Britte McBride, who conceived of the original courier-only model, also opposed a delay.
“I don’t think we can wait [to address] equity or the illicit market any longer,” she said.