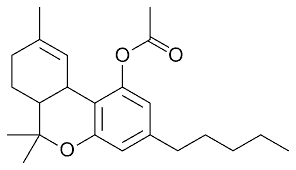
A better high than Delta 9?
According to user reports and the little science behind it, THC-O Acetate has been shown to be two to three times stronger than Delta 9 THC. You read that right. THC-O can be 300% more potent than traditional Delta 9 THC.
Users have claimed that THC-O Acetate is a much more introspective and psychedelic experience compared to Delta 9 or Delta 8 THC, which is likely due to the extreme potency. Similarly to Delta 8 THC, THC-O can only be made through isolation, which means most products will be either a vape cartridge or edibles.
While for most, normal Delta 8 or Delta 9 THC does the trick just fine and taking such a concentrated product would be excessive, there is a real appeal for medical applications of THC-O Acetate. For some, traditional Delta 9 doesn’t provide enough relief from pain, anxiety or other issues.
Due to its potency, many believe that THC-O could be a great beneficial medicine for those who want to use cannabis but need a more concentrated dose that isn’t easily attainable through traditional consumption. With that said, THC-O Acetate is treated similarly to Delta 8 currently.
That means in states where Delta 8 has already been banned, you may be unable to have THC-O products delivered, or find them at smoke shops. However since there is so little information on THC-O, few states actually know about it, which means distributors may be able to get away with it for a while.
Is THC-O Acetate the new designer drug?
Of course for now it is too soon to say if THC-O is likely to end up in a similar grave to Spice or K2. These were synthetically created cannabinoid products that ended up hurting a lot of people, leading them to be banned across the country. However the way these products skirted the law was by minutely adjusting their chemical makeups every time one was banned.
Because the government would ban specific makeups of these products, small adjustments made them different products technically. It is always possible, being a fully synthetic creation, that THC-O befalls a similar fate. In grey markets, profits typically rise above safety. As competition grows, just like Delta 8 became more widespread, the same will likely happen to THC-O Acetate.
Producers will try to create stronger and cheaper versions of the drug, the latter effort being that which leads to danger. We all saw what happened when illicit market vape cartridge producers tried to cut costs by including Propylene Glycol and Vitamin E Acetate in their products. This resulted in hundreds of hospitalizations and even deaths.
With any grey or black market cannabis products, it is always on the user to ensure they are getting a safe and reliable product. If demand for THC-O Acetate grows enough, you can bet there will be a market for it.
However as a non-natural cannabinoid, THC-O isn’t measured with most testing methods used for cannabis currently. While some have claimed to created a reliable process for measuring THC-O, nothing has become the standard. Due to this it might be a while before there are truly reliable providers of THC-O products, but that hasn’t stopped consumers before, and likely won’t this time around either.





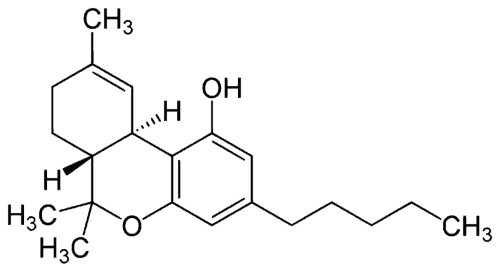 THC-O Acetate Molecule:
THC-O Acetate Molecule: