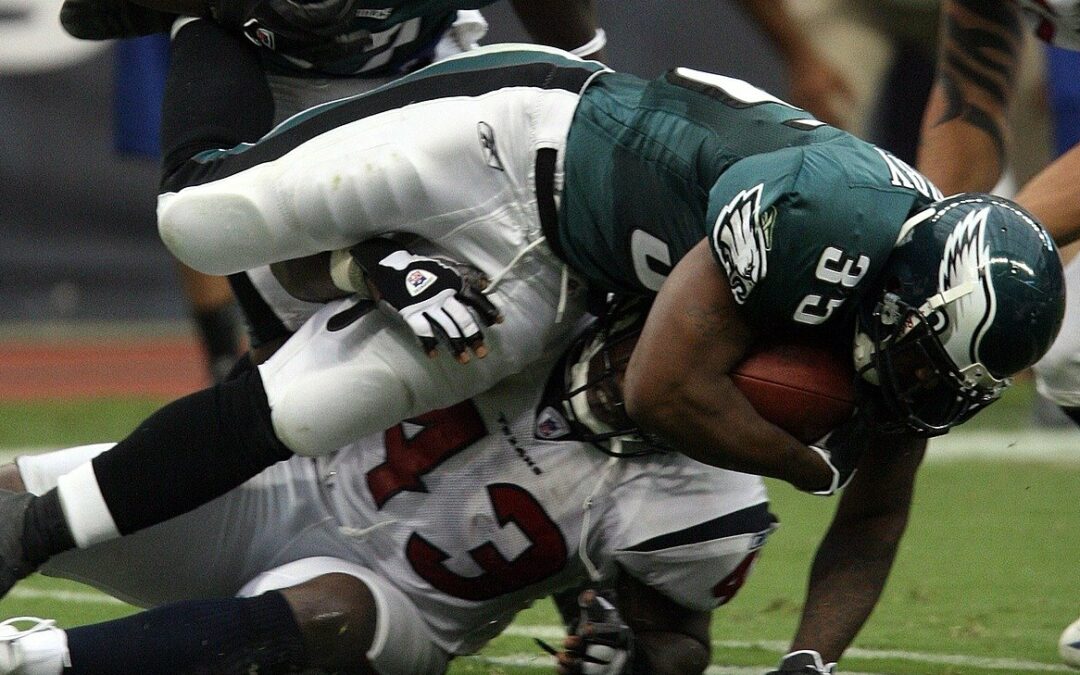
NFL to help fund research into cannabis treatment for concussions

Researchers from the University of Regina are getting more than $500,000 US from the National Football League to study the potential of using cannabinoids for the prevention and treatment of concussions.
Cannabinoids are the naturally occurring compounds found in the cannabis plant.
The NFL-NFLPA Joint Pain Management Committee, which said it wants to better understand and improve potential alternative pain management treatments for NFL players, put out a request for research proposals in June 2021.
The NFL said the U of R study is one of two to be awarded funding out of 106 submissions from top clinicians and researchers from around the world.
A study at the University of California San Diego that will be evaluating the effects of cannabinoids on pain and recovery from sports-related injuries in elite athletes is also receiving funding.
“We are grateful that we have the opportunity to fund these scientifically-sound studies on the use of cannabinoids that may lead to the discovery of data-based evidence that could impact the pain management of our players,” NFL chief medical officer Dr. Allen Sills said in a release.
The U of R study will be led by Patrick Neary, an exercise physiologist and professor in the faculty of kinesiology and health studies, who has been working in the area of concussion prevention and treatment for more than 15 years.
Neary said his team’s selection by the NFL was “extraordinary, overwhelming news” and “a very, very humbling experience.”
Looking for optimal CBD/THC formulation
His team will try to optimize the formulation of cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) for pain management in those suffering from post-concussion syndrome and chronic pain, and for a neuroprotective treatment for concussions.