Oklahoma Medical Marijuana Rundown

In June of 2018, Oklahoma surprised the country. The state voted to legalize medical marijuana.
Oklahoma medical marijuana State Question 788 was passed by the majority of people in the state, allowing the people to consume, grow and if licensed, sell medical marijuana.
The program is run by the Oklahoma Medical Marijuana Authority (OMMA), in conjunction with the Oklahoma State Department of Health to ensure regulatory oversight. Compared to other medical marijuana states, the Oklahoma medical marijuana program is pretty progressive.
Oklahoma Medical Marijuana Laws
Submitted as State Question 788, the people of Oklahoma passed a new section of law to be added to the Oklahoma Statutes. Section 420 of Title 63 permits an individual to posses a state issued medical marijuana license.
An Oklahoman with a medical marijuana license is allowed the following:
- To consume marijuana legally
- To possess up to 3 ounces of marijuana on their person
- To possess 6 mature marijuana plants
- To possess 6 seedling plants
- To possess 1 ounce of concentrates
- To possess 72 ounces of edibles, and
- To possess up to 8 ounces of marijuana in their residence.
However there were also changes to how possession of marijuana is handled in general. Being in possession of up to an ounce and half without a medical marijuana license is punishable by a $400 fine and a misdemeanor, if the subject can provide a medical condition. How strictly this will be enforced is yet to be seen.
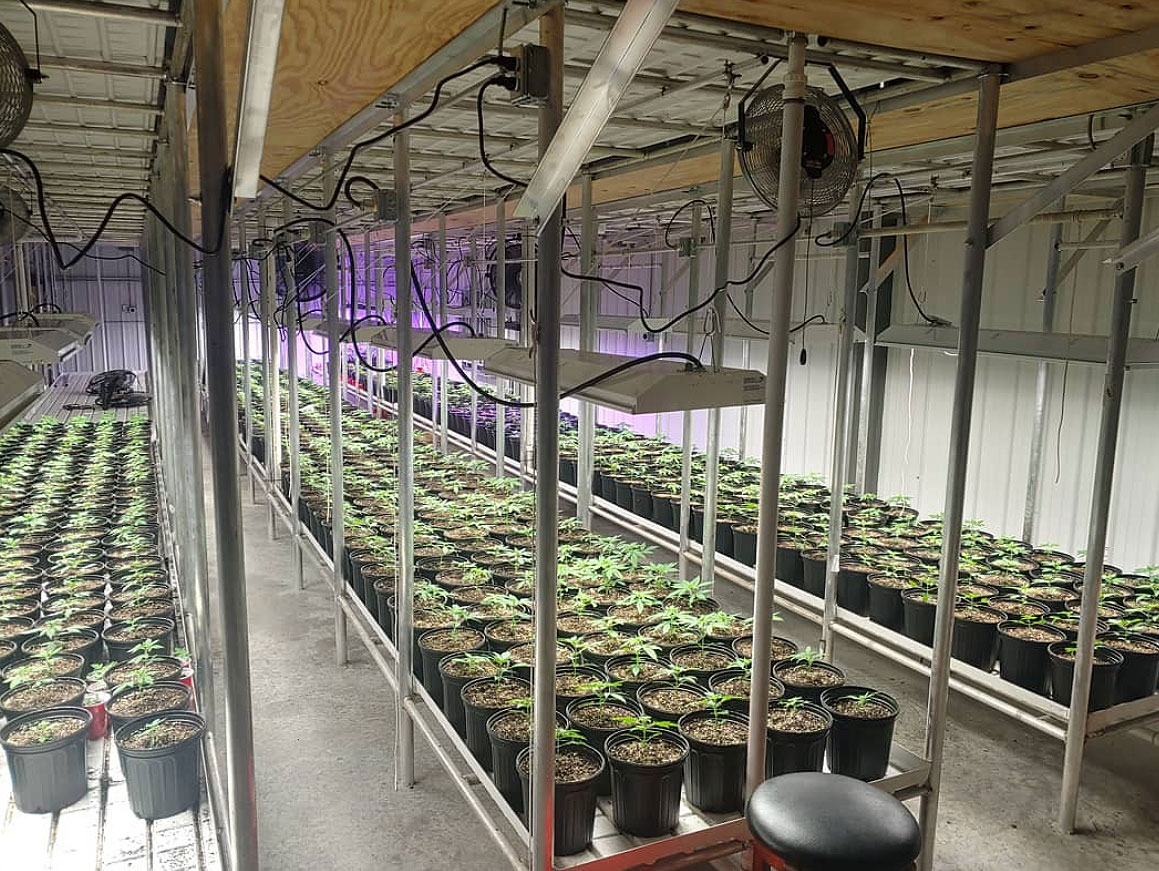

Individual and Business Licensing
Licenses for both Oklahoma medical marijuana patients and businesses are obtained through a straight forward application process. The applications are easily accessible on the OMMA page of the Oklahoma government website. It costs $200 for an individual to apply for a medical marijuana license, and only $20 to apply for those on Medicare and Medicaid.
To apply for dispensary, commercial growing, or processing permits, one must pay an application fee of $2,500. The requirements for obtaining these three business licenses are the same:
- Applicants must be 25 or older
- Applicants applying as an individual must show residency in the state of Oklahoma
- All applying members, managers and board members are Oklahoma residents
- An applicant can show ownership of non-Oklahoma residents, but that percentage of ownership cannot exceed 25%
- Applicants must be registered to conduct business in Oklahoma
- Applicants must disclose all ownership
- Applicants with nonviolent felony convictions in the last two (2) years, or applicants with any other felony conviction in five (5) years, inmates or anybody currently incarcerated is not qualified for a license.
In addition to these requirements, retailers must submit monthly reports to the Department of Health to keep track of weight sold, revenue and taxes. Commercial growers are restricted to only selling cannabis wholesale to licensed retailers. Growers will also submit monthly reports, detailing monthly yields, amount harvested in pounds, drying or dried marijuana on hand, amount sold to processors, amount of waste in pounds and more. However, there is no limit on the amount of cannabis a licensed grower can grow.
Processors are no different, and much submit a monthly report detailing the amount of marijuana purchased, amount of waste and wholesale sales to the Oklahoma Department of Health.
Oklahoma Medical Marijuana Applications
As of December 2018, over 22,000 people have been approved for personal Oklahoma medical marijuana licenses, 785 dispensaries have been licensed, and there are more than 1,200 licensed commercial growers and 270 licensed processors in the state. It hasn’t even been a year since Question 788 was approved, and Oklahoma is already kickstarting its medical marijuana industry.
Growers are pumping out close to 50 pounds a month already thanks to the regulation’s strict deadlines included by the people of Oklahoma that forced the state to accept applications within 60 days of Question 788’s passing. The state has already brought in $7.5 million from registration fees, and now that dispensaries have opened, the 7% sales tax will begin getting collected for additional revenue.
Is Oklahoma Ahead of The Curve?
Oklahoma medical marijuana has taken off more quickly than any other state program in the country. Less than 6 months after being passed, growers are growing, dispensaries are selling, and the people of Oklahoma are buying.
It’s possible that Oklahoma may be moving too fast. With no limit on how much a licensed grower can produce, the state may end up facing a similar issue to Oregon. Having too much marijuana and not enough people to buyl it might result in a collapse of the marketplace as the price of medical marijuana drops.
However as a medical marijuana program as opposed to Oregon’s recreational market, Oklahoma medical marijuana will be more strictly regulated by the Department of Health, which will hopefully push growers toward quality over quantity.
At the rate the Oklahoma medical marijuana industry is moving, it won’t be long before we see the first results of the new industry.