Areas With More Marijuana Dispensaries Have Fewer Opioid Deaths
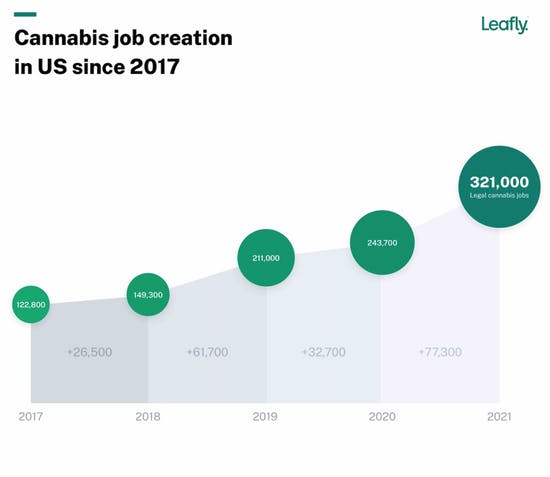
Increasing access to marijuana dispensaries is associated with a significant reduction in opioid-related deaths, according to a new study.
“Higher medical and recreational storefront dispensary counts are associated with reduced opioid related death rates, particularly deaths associated with synthetic opioids such as fentanyl,” the paper, published on Wednesday in the British Medical Association journal’s BMJ, concluded.
It’s a finding that “holds for both medical and recreational dispensaries,” the study says.
Researchers looked at opioid mortality and cannabis dispensary prevalence in 23 U.S.states from 2014 to 2018 and found that, overall, counties where the number of legal marijuana shops increased from one to two experienced a 17 percent reduction in opioid-related fatalities.
Increasing the dispensary count from two to three was linked to an additional 8.5 percent decrease in opioid deaths.
Further, the study found that this trend “appeared particularly strong for deaths associated with synthetic opioids other than methadone, with an estimated 21 percent reduction in mortality rates associated with an increase from one to two dispensaries.”
“If consumers use cannabis and opioids for pain management, increasing the supply of legal cannabis might have implications for fentanyl demand and opioid related mortality rates overall.”
“While the associations documented cannot be assumed to be causal, they suggest a potential association between increased prevalence of medical and recreational cannabis dispensaries and reduced opioid related mortality rates,” the researchers wrote. “This study highlights the importance of considering the complex supply side of related drug markets and how this shapes opioid use and misuse.”
This is far from the first piece of research to draw a connection between legal cannabis access and reduced harms from opioids. Multiple studies have found that marijuana effectively treats conditions like chronic pain for which opioids are regularly prescribed, and surveys show that many patients have substituted addictive painkillers with cannabis.
“Cannabis is generally thought to be a less addictive substance than opioids,” the new study says. “Cannabis can potentially be used medically for pain management and has considerable public support.”
“Our findings suggest that increasing availability of legal cannabis (modeled through the presence of medical and recreational dispensary operations) is associated with a decrease in deaths associated with the T40.4 class of opioids, which include the highly potent synthetic opioid fentanyl,” it continues. “This finding is especially important because fentanyl related deaths have become the most common opioid related cause of death.”
Earlier this month, a separate study determined that medical cannabis use is associated with significant reductions in dependence on opioids and other prescription drugs, as well as an increase in quality of life.